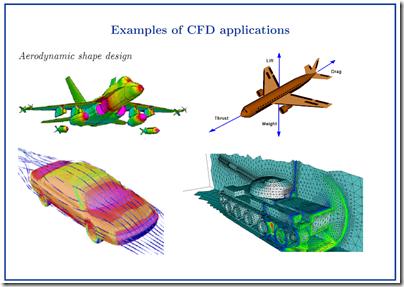
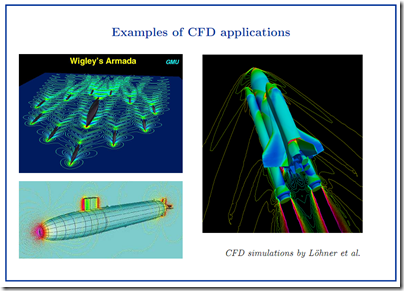
Some people feel difficult in install Fluent Program in their Computer, especially the function of each programs.
When you receive CD or DVD from Fluent, you must install 3 component to run Fluent completely, which is Gambit, Exceed and Fluent itself. Here’s the explanation of each program.
Installing Gambit
Gambit is drawing tool for Fluent. Here in Gambit, you can draw your object with a precise dimension, doing gridding and then specify Boundary Condition and Zone. That’s the 3 basic utilization of Gambit, and each step, you must specify well to simplify your next step in Fluent.
Gambit is easy, for expert of course. Yes, I can say this is easy, only for you that familiar with the interface. Actually you can use other drawing software such as AutoCAD, but in the process of import, sometimes didn’t match.
Install Gambit is easy, just follow the instruction.
Installing Exceed
Exceed is XWindows. You must install this program when you use Microsoft Windows for your operating system. If you omit this program, Gambit would not run. This is because Gambit actually written for UNIX.
To Install Exceed, follow the instruction
Installing Fluent
Fluent is processing and post-processing software. Your drawing usually in .msh extension, will be imported in Fluent and then, specify the problem, running simulation, and post-processing, including showing result in many forms.
Installing Fluent is simple, just follow the instruction.
Putting Key
Fluent record your LAN Card Serial Number to incorporated in your key. This to ensure that you can only install Fluent in 1 Computer. So, if there’s problem with your Fluent Key, check your LAN. You can ask another key if you send them good reason to do so.
Just put license key in .dat extension to /license folder.